WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO TALK ABOUT AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES?
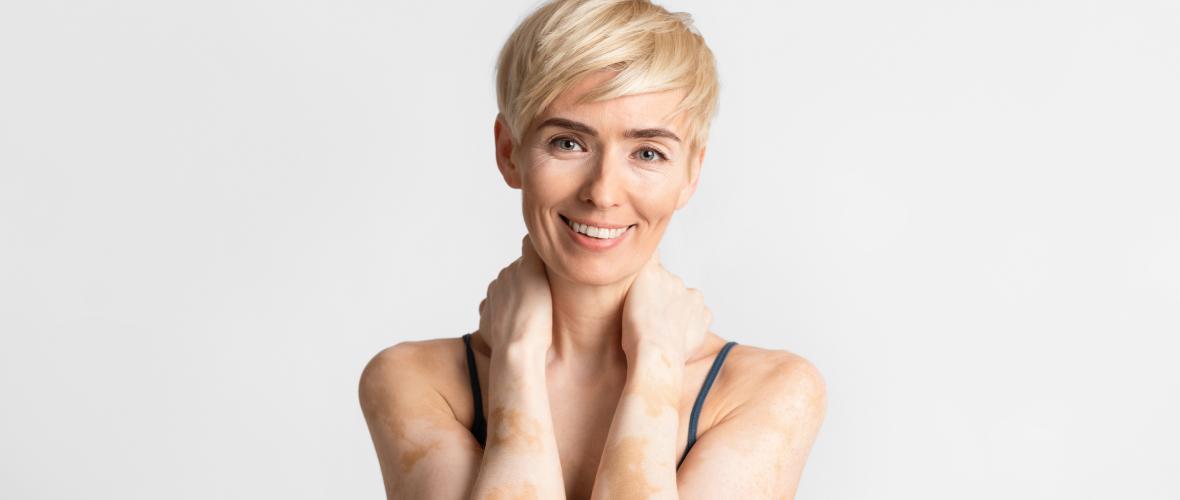

< p>Autoimmune diseases are represented as a condition in which the immune system attacks its own healthy tissues because it mistakes them as foreign tissues. Most autoimmune pathologies generate inflammation that damages many organs. The usual signs and indications are fatigue, fever, muscle pain, joint pain and swelling, dermal problems, belly pain, digestive problems and enlarged glands.
Diet is a fundamental pillar, as well as exercise, in addition to nutrients involved in the proper preservation of the immune system, are the pillars of good health.
Many international scientific societies recognize that several vitamins or minerals (copper, folate, iron, selenium, zinc or vitamins A, B6, B12, C and D) are involved in the proper performance of the immune system. In a situation of clear deficiency of a nutrient involved in the immune system, taking it can have an impact on the immune response. They also point out that the intake of vitamin C helps with the optimization of the immune system.
How does stress affect the immune system?
Although this can harm all organs and organic functionalities, its effects are concentrated on the heart and cardiovascular system, which is forced to work harder, and on the immune system, which decreases its effectiveness. In cases of stress cortisol is released, this hormone increases the participation of our body in an intense way, cortisol can cause harmful effects on the immune system, favoring a greater predisposition to get sick.
What are considered autoimmune diseases?
An autoimmune disease is a condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the human body. The immune system commonly safeguards against germs such as bacteria and viruses. Once it detects such foreign invaders, it sends a battalion of military cells to attack them. Commonly, the immune system can distinguish between foreign cells and its own cells. In an autoimmune pathology, the immune system takes certain body parts, such as joints or the dermis, as foreign.
Nevertheless, several people are more likely to develop an autoimmune pathology than others. According to a 2014 analysis, ladies possess twice the chance of getting autoimmune pathologies compared to men: 6.4% of females compared to 2.7 % of men. The pathology starts throughout a lady's childbearing age (between the ages of 15 and 44). Several autoimmune pathologies are more frequent in certain ethnic groups. Certain autoimmune pathologies, such as multiple sclerosis and lupus, are hereditary. Not all members of the nuclear family will have precisely the same pathology, but they will inherit the predisposition to an autoimmune pathology. Since the incidence of autoimmune pathologies is increasing, scholars suspect that environmental components such as infections and exposure to chemicals or solvents may also be related.